
Demystifying the 20%: Men with Autoimmune Conditions
Men and autoimmune conditions aren’t two things commonly put together, and that’s often because autoimmune diseases are significantly more prevalent in women.
However, men still make up about 20% of those living with these conditions.
By shedding light on men’s experiences, we can better understand these diseases and improve support for everyone affected.
Discussing men’s experiences with autoimmune diseases is crucial.
- First, it helps raise awareness that these conditions don’t exclusively affect women.
- Second, it sheds light on the unique challenges men face in managing their symptoms and seeking treatment.
- Finally, it encourages more research and better healthcare practices tailored to men’s needs, ultimately improving their quality of life.
By understanding and addressing the specific experiences of men with autoimmune diseases, we can ensure more inclusive and effective support for everyone affected.
Prevalence and Common Autoimmune Diseases in Men
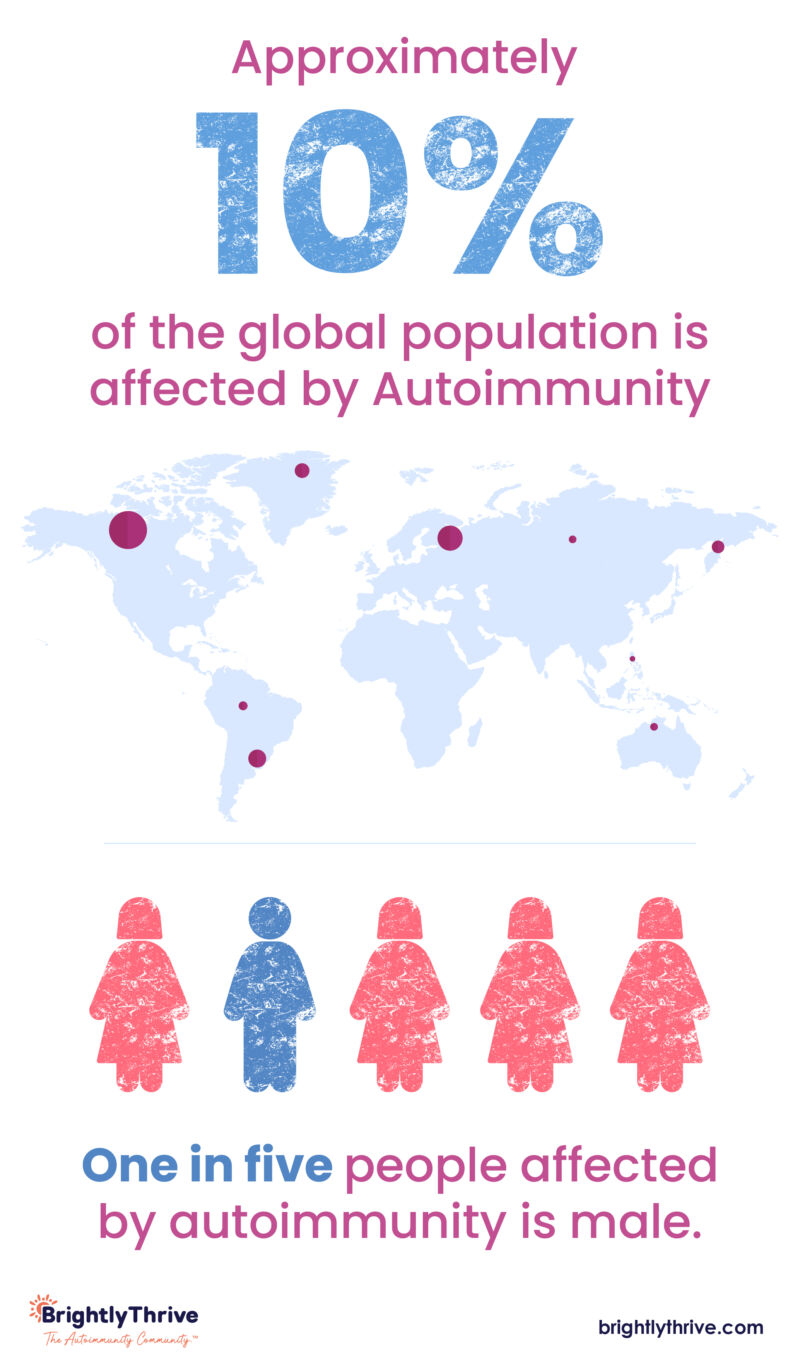
This translates to millions of men worldwide living with these challenging conditions.
Overview of Common Autoimmune Diseases Affecting Men
Did you know that autoimmune diseases can strike anyone, regardless of gender?
While often considered a women’s health issue, these mysterious conditions also impact a significant number of men.
- Addison’s Disease: This rare disorder occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough hormones. It affects both men and women equally, leading to symptoms like fatigue, muscle weakness, and low blood pressure.

- Celiac Disease: An autoimmune disorder where the ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine. Celiac disease can affect anyone, but men often experience more severe symptoms and complications.

- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): MS is a condition where the immune system attacks the protective covering of nerves. While it is more common in women, men with MS often have a more aggressive disease course and a worse prognosis.

- Lupus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, SLE): Around 90% of individuals with lupus are women, but men can and do develop the disease. Lupus can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, and internal organs, leading to widespread inflammation and damage.

- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): This includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, both of which cause chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. IBD affects men and women equally, but men may experience more complications and require more aggressive treatment.

Factors Contributing to Gender Differences
Genetic Factors:
The presence of two X chromosomes in women contributes to a higher prevalence of autoimmune diseases.
The X chromosome carries a significant number of immune-related genes, which may explain the higher susceptibility in women.
Men, having one X and one Y chromosome, have fewer of these immune-related genes.
Hormonal Influences
Hormones such as estrogen can influence immune system activity, potentially making women more susceptible to autoimmune diseases.
Conversely, the lower levels of these hormones in men may offer some protection.
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Both genetic predisposition and environmental triggers such as infections, stress, and lifestyle choices play a role in the development of autoimmune diseases.
These factors can affect both men and women, though their impacts may differ based on genetic and hormonal differences.
Challenges in Diagnosis and Treatment for Men
Underdiagnosis
One of the major hurdles men face with autoimmune diseases is underdiagnosis. This issue arises due to several factors:
- Men’s Reluctance to Seek Medical Care: Men are often less likely to visit a doctor when they experience symptoms. This reluctance can stem from societal norms and expectations about masculinity, where men may feel pressure to “tough it out” rather than seek help.
- Healthcare Providers’ Biases: There can be an implicit bias among healthcare providers that autoimmune diseases are predominantly women’s issues. As a result, symptoms in men might be overlooked or misattributed to other causes, delaying accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Healthcare Utilization
Another challenge is the lower rate of healthcare utilization among men. This includes:
Fewer Regular Checkups and Preventive Care Visits: Men are less likely to attend regular health checkups and preventive care appointments compared to women. This lack of routine healthcare means that early signs of autoimmune diseases may go unnoticed, leading to more advanced disease by the time of diagnosis.
Social and Psychological Factors
Social and psychological factors also play a significant role in the challenges men face with autoimmune diseases:
Stigma Around Discussing Symptoms and Seeking Help: There is often a stigma associated with discussing health issues and seeking help, particularly among men. This stigma can prevent men from voicing their concerns and symptoms, further contributing to delays in diagnosis and treatment.
Male Celebrities with Autoimmune Conditions
Ashton Kutcher (Vasculitis)
Ashton Kutcher, the popular actor known for his roles in “That ’70s Show” and “Two and a Half Men,” has openly shared his battle with vasculitis.
Vasculitis is a rare condition where the blood vessels become inflamed, leading to various complications such as restricted blood flow, tissue damage, and organ issues.
Kutcher’s experience has brought much-needed attention to this lesser-known autoimmune disease.
Nick Cannon (Lupus)
Entertainer Nick Cannon, famous for his work on “Wild ‘N Out” and “America’s Got Talent,” was diagnosed with lupus nephritis, a severe form of lupus that affects the kidneys.
Cannon has been vocal about his health journey, raising awareness about lupus and emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis and proper management of the disease.
Phil Mickelson (Psoriatic Arthritis)
Golf legend Phil Mickelson has dealt with psoriatic arthritis, an autoimmune disease that causes joint pain and inflammation.
Despite the challenges posed by this condition, Mickelson has continued to excel in his sport, demonstrating resilience and the ability to manage his symptoms effectively while maintaining a high level of performance.
Morgan Freeman (Fibromyalgia)
Acclaimed actor Morgan Freeman has openly discussed his struggles with fibromyalgia, a condition characterized by widespread pain, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties. Freeman’s openness about his fibromyalgia has helped to destigmatize the condition and bring greater awareness to the challenges faced by those living with chronic pain and autoimmune diseases.
Montel Williams (Multiple Sclerosis)
Television host Montel Williams was diagnosed with multiple sclerosis (MS) in 1999.
MS is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, muscle weakness, and coordination issues.
Williams has become a prominent advocate for MS awareness, using his platform to educate others about the disease and support those affected by it.
Did you know that one of our very own ThriveGuides™, Christina Tidwell, had the opportunity to talk to Montel Williams about his story and advocacy on MS?
Check it out here:
Specific Considerations in Managing Autoimmune Diseases in Men
Understanding the unique challenges men face with autoimmune diseases is crucial for providing effective care. By addressing these tailored needs, we can improve health outcomes and quality of life for men living with autoimmune conditions.
1. Diagnosis and Screening
Men with autoimmune diseases often face unique challenges when it comes to diagnosis and screening.
Healthcare providers need to maintain a higher index of suspicion due to the lower prevalence of these conditions in men.

This vigilance is crucial to avoid potential delays in diagnosis, which can occur because autoimmune diseases are more commonly associated with women.
The Autoimmune Association (formerly American Autoimmune Related Diseases Association [AARDA]) reports that patients typically consult four different doctors over an average period of 4.5 years before getting diagnosed.
Early detection is key to managing symptoms effectively and preventing disease progression.
2. Severity and Progression
Autoimmune diseases in men can sometimes present with more severe organ involvement, particularly in conditions like lupus.
This increased severity necessitates more aggressive treatment strategies and closer monitoring to manage the disease effectively.
Understanding these differences helps tailor treatment plans to meet the specific needs of men, ensuring better health outcomes.

3. Hormonal Considerations
Hormones play a significant role in autoimmune diseases.
Testosterone, for instance, has a protective effect against some autoimmune conditions.
Monitoring and addressing hormonal imbalances in men is essential for managing their symptoms and improving their overall health.
This includes considering how treatments might impact hormone levels and making necessary adjustments.

4. Cardiovascular Risk
Men with autoimmune diseases often have different cardiovascular risk profiles compared to women.
Thorough cardiovascular health assessments and preventive measures are vital to address these risks.
This includes regular monitoring of heart health and implementing strategies to reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications, which can be more pronounced in men with autoimmune conditions.

5. Fertility and Family Planning
Autoimmune diseases and their treatments can impact fertility.
Counseling men on the potential effects of their condition and treatment options on fertility is crucial.
This ensures that they are informed about their options and can make decisions that align with their family planning goals.

6. Research Participation
Encouraging male participation in clinical trials is important for understanding how autoimmune diseases affect men differently.
Increased participation helps generate more comprehensive data, leading to better, more tailored treatments and care strategies for men with autoimmune conditions.

7. Psychosocial Support
Men with autoimmune diseases often face unique psychological challenges.
Addressing these challenges by providing mental health support and resources tailored to men is essential.
This includes creating a supportive environment where men feel comfortable discussing their symptoms and seeking help.

8. Tailored Treatment Approaches
Adjusting dosages and medication choices based on male-specific factors is crucial for effective treatment.
Men may respond differently to certain medications, and their treatment plans should reflect these differences to ensure the best possible outcomes.

9. Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications, particularly in exercise, are important for managing autoimmune diseases in men.
Recommendations for men often include engaging in 300 minutes of moderate to vigorous activity per week.
This level of activity helps manage symptoms, improve overall health, and reduce the risk of complications associated with autoimmune diseases.

Final Thoughts
It’s important to address autoimmune diseases in men to make sure everyone gets the care and support they need.
By spreading awareness and encouraging proactive healthcare, we can help men recognize symptoms sooner, get timely treatment, and manage their conditions better.
Living with an autoimmune disease can be tough, but with the right support and resources, men can still have fulfilling, healthy lives.
At BrightlyThrive™, we provide a safe space not only for women, who are more often affected by autoimmunity, but also for men, who may not always get the attention their health deserves.
Let’s keep talking about these issues and encourage men to take charge of their health, knowing they are not alone on this journey.

Ready to take the next step in your health journey? Become a member of BrightlyThrive™ today! Join a supportive community where you can find resources, share your wisdom and experiences, and connect with others who understand what you’re going through.
References
Autoimmune Diseases. (n.d.). National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences. https://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/topics/conditions/autoimmune
Common Autoimmune Diseases in Men. (n.d.). Amy Myers MD. https://www.amymyersmd.com/article/autoimmune-diseases-in-men
Professional, C. C. M. (n.d.-b). Autoimmune Diseases. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21624-autoimmune-diseases
Team, M. S. M. (2021, February 11). Men’s Health: Autoimmune Disease | Main Street Medical Clinics, Houston. Main Street Medical Clinic. https://www.mainstreetclinics.com/blog/autoimmune-disease/mens-health-autoimmune-disease/
Kmiecik, C. (2022, June 29). Men Get Autoimmune Disease, Too. Autoimmune Association. https://autoimmune.org/men-get-autoimmune-disease-too/
Watson, S. (2024, March 4). Everything to Know About Autoimmune Diseases. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/autoimmune-disorders
Selmi, C., Cincinelli, G., Generali, E., Dudam, R., & Ravindran, V. (2018). Why women or why not men? sex and autoimmune diseases. Indian Journal of Rheumatology/Indian Journal of Rheumatology, 13(1), 44. https://doi.org/10.4103/injr.injr_1_18
TAGS:
CATEGORIES:






